What is Conveyor Belt Tensile Strength and Elongation at Break?
In technical descriptions of rubber conveyor belts, we often encounter terms like elongation at break, full thickness elongation at break, and tensile strength. These parameters respectively represent what characteristics of the rubber conveyor belt? And what are the differences between them?
1.What is elongation in rubber?
Elongation in rubber refers to the deformation of the material when subjected to external force, expressed as the ratio of the deformation to the original length, usually in percentage. For example, if a rubber with a length of 100 millimeters is stretched to 110 millimeters, the elongation is 10%. The elongation in rubber is influenced by factors such as molecular structure, hardness, temperature, and humidity.
Elongation in rubber is also an important indicator of its material properties. Rubber with high elongation typically exhibits good elasticity and flexibility, allowing it to undergo significant deformation without immediate rupture. This property is particularly important in applications such as springs, seals, and rubber hoses.
2.What is elongation at break in rubber?
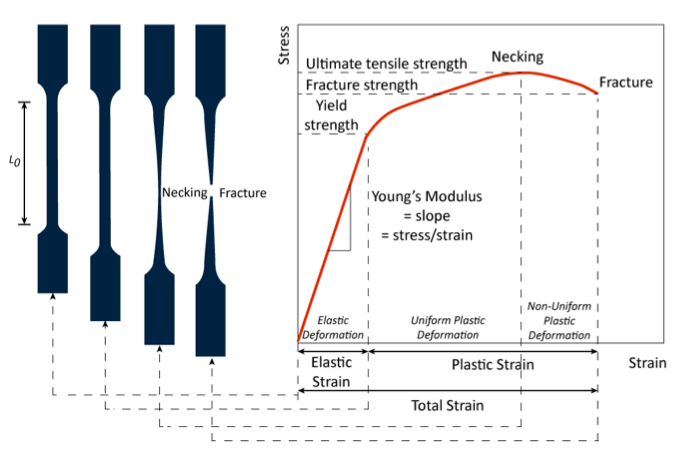
Elongation at break (also known as elongation at fracture) in rubber refers to the maximum deformation the rubber sample undergoes before fracturing when subjected to tension, expressed as the ratio of the increased length to the original length, usually in percentage. It indicates the maximum extent of deformation the rubber can withstand before failure. The unit remains as a percentage (%).

For example, if the initial length of a rubber strip is 10 centimeters and it stretches to a length of 20 centimeters before breaking, the elongation at break is 100%, meaning the length doubles before fracture.
The full-thickness elongation at break of a rubber conveyor belt refers to the ratio of the length increase of the rubber sample when stretched to break in the direction of the overall thickness of the rubber material (including the EP layer) to the original length, usually expressed as a percentage. Unlike conventional elongation at break, full-thickness elongation at break takes into account the deformation of the rubber in the overall thickness direction. The unit is still percentage (%)
Elongation at break in the cover rubber of conveyor belts is a crucial indicator of the material’s extensibility and toughness. Rubber with high elongation at break typically exhibits excellent stretching performance, able to undergo significant deformation under load without immediate fracture. This property is crucial in applications that undergo frequent stretching or twisting forces, such as conveyor belts, rubber bands, and rubber hoses.
3.What is tensile strength in rubber?
Tensile strength in rubber refers to the maximum tensile force the rubber can withstand before fracturing when subjected to tension. It is typically expressed in Pascals (Pa) or megapascals (MPa), with 1 MPa equal to 1 N/m².
For example, if a rubber material has a tensile strength of 10 MPa, it means it can withstand a pressure of 10 megapascals per square meter before fracturing when subjected to tension. Exceeding this limit can lead to rupture or deformation.
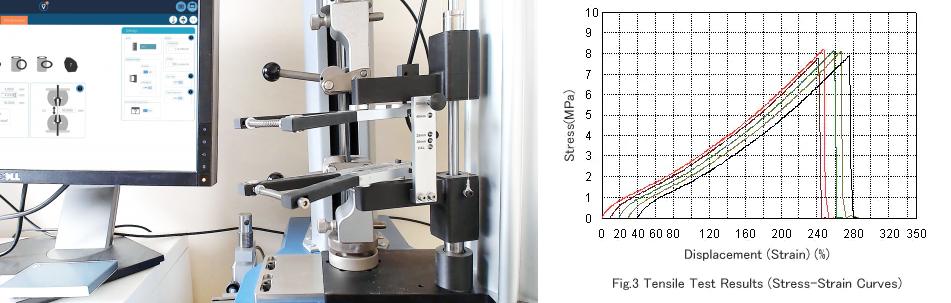
For example, suppose there is a rubber material with a tensile strength of 10 MPa (MPa), which means that during the stretching process, each square meter of rubber can withstand a pressure of 10 MPa. If we apply a tensile force of more than 10 MPa to this rubber, it may break or deform. In the technical description of the conveyor belt covering rubber, tensile strength is the most common and important technical indicator. This indicator It often directly determines the quality of the conveyor belt. In the conveyor belt standards of various countries, tensile strength is used as the primary indicator. For example, DIN-Z in DIN22102 indicates that the tensile strength of the covering rubber of this conveyor belt is 25Mpa. In the AS standard, AS-N indicates that the tensile strength is 17Mpa.
4. The relationship among tensile strength, elongation and elongation at break of conveyor belts
The elongation at break and tensile strength of rubber conveyor belts are closely related. Only when the test sample is not destroyed during the stretching process can it indicate a higher elongation. Therefore, having a higher tensile strength is a necessary condition for achieving a high elongation at break. Additionally, the elongation at break decreases with increasing tensile stress and hardness, while it increases with increasing elasticity. Rubber with good molecular chain flexibility and high elasticity exhibits a higher elongation at break. Natural rubber (NR) is most suitable for producing products with high elongation, with the elongation at break increasing as the rubber content increases. When the rubber content is around 80%, the elongation at break can reach up to 1000%. Rubber that undergoes plastic deformation easily also exhibits a higher elongation at break, such as isobutylene-isoprene rubber (IIR), which can achieve a relatively high elongation at break.
Tensile strength in rubber is determined by material properties such as composition, manufacturing process, and temperature. Generally, higher tensile strength indicates better resistance to deformation and stability under tension.
The elongation at break decreases with increasing cross-linking density. Therefore, when manufacturing products with high elongation, the amount of vulcanizing agent and accelerator should be appropriately reduced. Reinforcing agents decrease the elongation at break, especially carbon black with small particle size and high structure, which causes a more significant decrease in the elongation at break. As the filler content increases, the elongation at break decreases. Increasing the amount of plasticizer can also achieve a larger elongation at break.
Generally, the elongation, elongation at break, and tensile strength of rubber conveyor belts specifically refer to the characteristics of the rubber cover layers, including the top rubber cover and bottom rubber cover. Meanwhile, the full thickness elongation at break refers to the overall properties of the conveyor belt, including the EP layer.
In summary, elongation, elongation at break, and tensile strength are important indicators of the elasticity and durability of rubber materials in conveyor belts. Choosing the appropriate rubber material and processing techniques can effectively enhance the overall performance and service life of conveyor belts.
SUNGDA CONVEYOR BELT CO.,LTD.








Tags: conveyor belt specification,elongation at break,EP conveyor belt,Rubber conveyor belt,TENSILE STRENGTH